Did you know that...
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is currently considered to be the leading cause of vision loss after 65 years of age. There are estimated 50 million individuals suffering from AMD.
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is currently considered to be the leading cause of vision loss after 65 years of age. There are estimated 50 million individuals suffering from AMD.
Age-related macular degeneration is a chronic progressive disease of the macula (the central part of the retina), which is responsible for visual acuity, detail recognition and colour and contrast vision.
There are two types of macular degeneration:
– dry AMD (85-90% of all cases)
Dry AMD is characterised by slow progression and does not lead to sudden deterioration of visual acuity. Image deformations and local spots of vision loss can occur.
– wet AMD, which is associated with the presence of subretinal neovascular membrane. The course of the disease is rapid, and is usually associated with sudden deep loss of central vision.
The primary method of treatment for wet AMD is intravitreal anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) therapy, which inhibits the growth of subretinal neovascular membrane.
The primary aim of the therapy is to stop the disease from progressing. The treatment usually involves a few injections. The number, type and frequency of injections is decided on by the attending doctor.
The Ophthalmology Department of the St. Adalbert’s Hospital offers the new BEOVU (brolucizumab) treatment for wet AMD.
The first dose already stops disease progression! The treatment visibly reduces neovascular changes, and decreases the growth rate of endothelial cells and vascular permeability.
When administered into the vitreous body, the new generation molecule stops the activation of VEGF receptors.
The use of the drug ensures that normal anatomical features of the retina are maintained.
Treatment regimen:
At the beginning of the treatment, the drug is administered at monthly intervals. After 3 months, it is only given once every quarter. Lower frequency of administration has a significant effect on patient comfort and safety.
EYLEA® is a VEGF inhibitor. VEGF inhibitors stop the action of the vascular endothelial growth factor. By doing so, EYLEA® protects your vision. EYLEA® blocks a certain protein that leads to the formation of leaking blood vessels. The active substance in the medicine is aflibercept. Aflibercept reduces retinal oedema (swelling) and protects your vision.
Treatment regimen:
At the beginning of treatment, injections are given every 4 weeks. After 3 months, the drug is injected into the vitreous body every 8 weeks. In the second year of treatment, the injections are administered once a quarter.
Eylea has a benefit of less frequent eye injections with similar efficacy.
Lucentis recognises and binds a specific protein, vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A) present in the eye. By binding VEGF, Lucentis can prevent abnormal vascular growth and oedema. The active substance in the medicine is ranibizumab.
Injections are administered at about 4-week intervals.
The active substance in AVASTIN is bevacizumab, which blocks vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A). AVASTIN is not licensed for use in wet AMD, but it is used all over the world for this condition as an off-label drug (beyond the officially approved indications). You need to provide your consent for the use of this medicine to treat your condition.
AVASTIN is used by ophthalmologists all over the world in their everyday practice.
Ozurdex is a dexamethasone derivative. The medicine is manufactured as an implant and is licensed for being placed inside the eye. The implant looks like a lead from a mechanical pencil, but is white in colour. The substance contained in Ozurdex is different from triamcinolone in that it does not cause floaters to develop after being injected into the eyeball. Ozurdex is active for 4 to 6 months.
The procedure is performed in outpatient settings.
Before injection, eye drops will be administered which dilate the pupils and numb the eye.
The ophthalmologist performs an injection during which the medicine is delivered to the vitreous chamber.
There is no pain associated with the procedure. You may only feel a slight stinging sensation.
The procedure itself takes about 5 minutes.
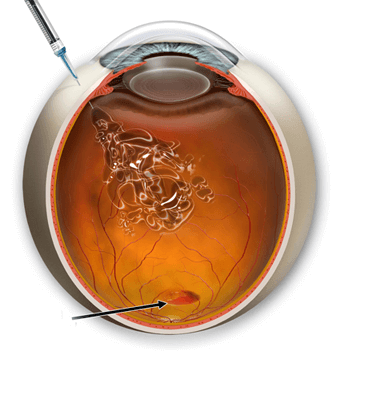
You should follow your doctor’s instructions. After the procedure, your eye may be red and sensitive.
Wielkopolskie Centrum Medyczne
Sp z o.o. S.K.A
st. Bolesława Krzywoustego 114
61-144 Poznań, POLAND
Hospital hours:
Mon-Fri 8:00 – 20:00
Sat 8:00 – 16:00
Contact us to arrange a visit or to learn more!
Write to us